Preprint: How redundant is the Transformer stack in speech representation models?
The paper (preprint) is available on arXiv.
A workshop version of this paper is to be presented at the Workshop on Efficient Natural Language and Speech Processing (ENLSP) @ NeurIPS, Vancouver, Canada, 2024. Paper and poster URL will be available soon.
Abstract
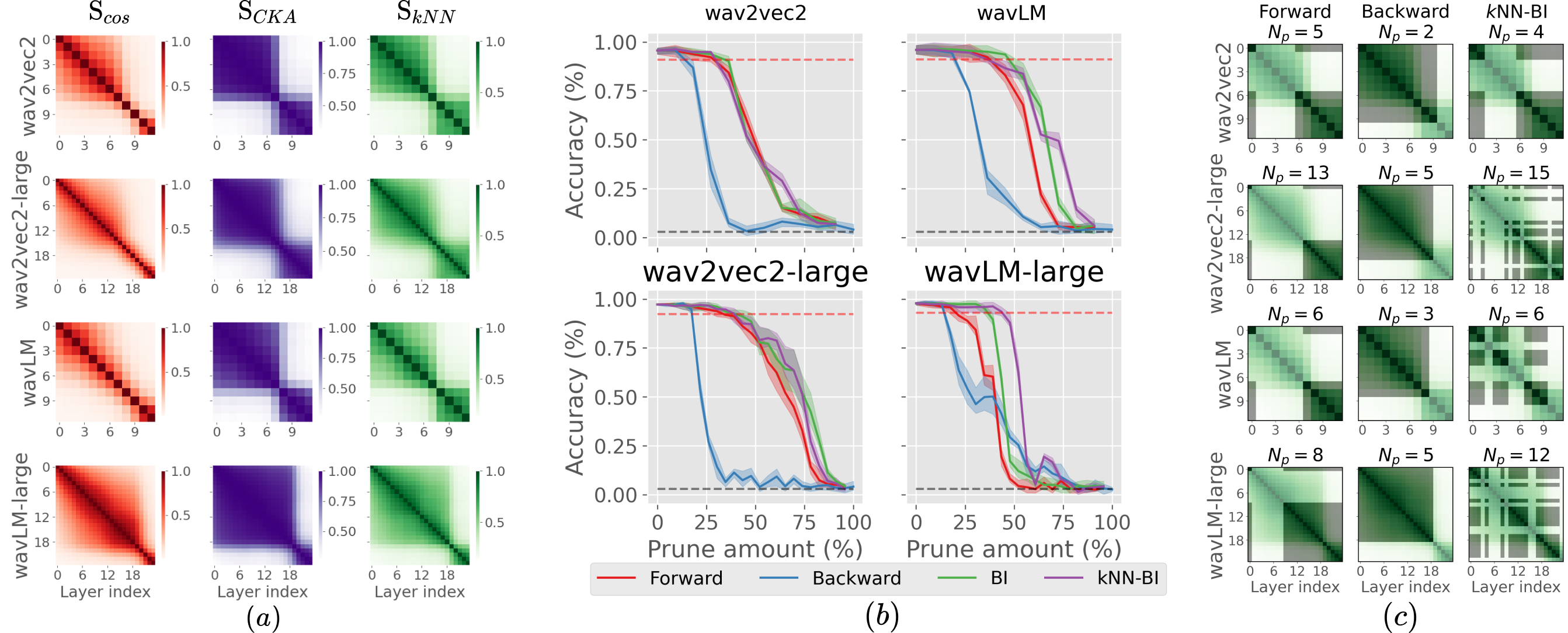
Self-supervised speech representation models, particularly those leveraging transformer architectures, have demonstrated remarkable performance across various tasks such as speech recognition, speaker identification, and emotion detection. Recent studies on transformer models revealed high redundancy between layers and the potential for significant pruning, which we will investigate here for transformer-based speech representation models. We perform a detailed analysis of layer similarity in speech representation models using three similarity metrics: cosine similarity, centered kernel alignment, and mutual nearest-neighbor alignment. Our findings reveal a block-like structure of high similarity, suggesting two main processing steps and significant redundancy of layers. We demonstrate the effectiveness of pruning transformer-based speech representation models without the need for post-training, achieving up to 40% reduction in transformer layers while maintaining over 95% of the model’s predictive capacity. Furthermore, we employ a knowledge distillation method to substitute the entire transformer stack with mimicking layers, reducing the network size by 95-98% and the inference time by up to 94%. This substantial decrease in computational load occurs without considerable performance loss, suggesting that the transformer stack is almost completely redundant for downstream applications of speech representation models.